How to Succeed in Algorithms Interview Series
Applications of Stack
- parentheses
- calculator: +-*/
- priority
Implementation Detail of Using Stack
- Use ArrayDeque or LinkedList
- we can push/pop at both ends
- what to store in stack, its meaning
- when to pop out
Examples of Using Stack
- LeetCode 1003 - Check If Word Is Valid After Substitutions
- LeetCode 394 - Decode String
- countStack, resStack
每次遇到“[”就把“[”之前的res塞进stack里,遇到数字就把数字塞进numStack里,每次遇到“]”就把stack.pop()和numStack.pop()个res连起来,然后作为新的res,等待下一次被塞进stack里,或者被和stack里的元素连接起来,最后返回res即可if the current char is ‘[’(next is a char ), push res to strStack, clean res; if the current char is ‘]’ (build the res string), append res to previous string in strStack
- countStack, resStack
- LeetCode 32 - Longest Valid Parentheses SubString
if s[i] is ')' If s[i-1] is '(', longest[i] = longest[i-2] + 2 Else if s[i-1] is ')' and s[i-longest[i-1]-1] == '(', longest[i] = longest[i-1] + 2 + longest[i-longest[i-1]-2]public int longestValidParentheses(String s) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); int max=0; int left = -1; for(int j=0;j<s.length();j++){ if(s.charAt(j)=='(') stack.push(j); else { if (stack.isEmpty()) left=j; else{ stack.pop();//\\ if(stack.isEmpty()) max=Math.max(max,j-left); else max=Math.max(max,j-stack.peek()); } } } return max; }
Stack + Greedy
- 运用Stack加贪心法的题目有很多,这类问题的做法是遍历输入数组,当前元素与栈顶元素比较,如果当前元素更优则pop栈顶元素,直到栈顶元素更优为止,而后插入当前元素。
- LeetCode 316 - Remove Duplicate Letters
public String removeDuplicateLetters(String sr) {
int[] res = new int[26]; //will contain number of occurences of character (i+'a')
boolean[] visited = new boolean[26]; //will contain if character (i+'a') is present in current result Stack
char[] ch = sr.toCharArray();
for(char c: ch){ //count number of occurences of character
res[c-'a']++;
}
Stack<Character> st = new Stack<>(); // answer stack
int index;
for(char s:ch){
index= s-'a';
res[index]--; //decrement number of characters remaining in the string to be analysed
if(visited[index]) //if character is already present in stack, dont bother
continue;
//if current character is smaller than last character in stack which occurs later in the string again
//it can be removed and added later e.g stack = bc remaining string abc then a can pop b and then c
while(!st.isEmpty() && s<st.peek() && res[st.peek()-'a']!=0){
visited[st.pop()-'a']=false;
}
st.push(s); //add current character and mark it as visited
visited[index]=true;
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//pop character from stack and build answer string from back
while(!st.isEmpty()){
sb.insert(0,st.pop());
}
return sb.toString();
}- LeetCode 654 - Maximum Binary Tree
- decreasing stack
- create the TreeNode while access the data, push them into monotone stack, connect TreeNodes when push or pop
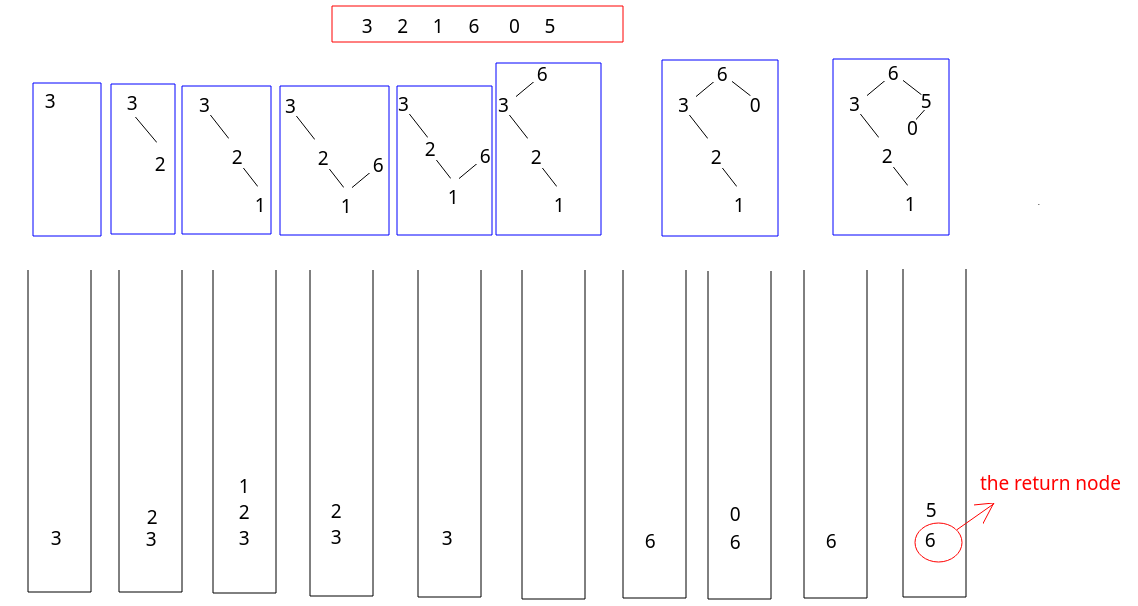
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) { Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>(); for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { TreeNode curr = new TreeNode(nums[i]); while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().val < nums[i]) { curr.left = stack.pop(); } if(!stack.isEmpty()) { stack.peek().right = curr; } stack.push(curr); } return stack.isEmpty() ? null : stack.removeLast(); } - decreasing stack
Examples
- LeetCode 591 - Tag Validator
- LeetCode 71 - Simplify Path
- LeetCode 636 - Exclusive Time of Functions: stack + prevTime
- LeetCode 946 - Validate Stack Sequences
- Keep pushing pushed elements into stack if the top element on the stack is different from the current one of popped;
- Keep poping out of the top element if it is same as the current one of popped;
- Keep pushing pushed elements into stack if the top element on the stack is different from the current one of popped;
- LeetCode 394 - Decode String
- Implement k stacks in a single array
- Stack Reversal
public void reverseStack(Stack<Integer> stack){
if(stack.isEmpty())
return ;
int val= stack.pop();
reverseStack(stack);
pushToBottom(stack,val);
return ;
}
private void pushToBottom(Stack<Integer> stack,int item){
if(stack.isEmpty()){
stack.push(item);
return ;
}
int val= stack.pop();
pushToBottom(stack,item);
stack.push(val);
}- LeetCode 889 - Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Postorder Traversal
public TreeNode constructFromPrePost(int[] pre, int[] post) { Deque<TreeNode> s = new ArrayDeque<>(); s.offer(new TreeNode(pre[0])); for (int i = 1, j = 0; i < pre.length; ++i) { TreeNode node = new TreeNode(pre[i]); while (s.getLast().val == post[j]) { s.pollLast(); j++; } if (s.getLast().left == null) s.getLast().left = node; else s.getLast().right = node; s.offer(node); } return s.getFirst(); } - LeetCode 255 - Verify Preorder Sequence in Binary Search Tree
public boolean verifyPreorder(int[] preorder) { Stack<Integer> stk = new Stack<Integer>(); int min = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for(int num : preorder){ if(num < min) return false; while(!stk.isEmpty() && num > stk.peek()){ min = stk.pop(); } stk.push(num); } return true; } public boolean IsValidPostOrderBst(int[] nums) { int i = nums.length; int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int j = nums.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) { if (nums[j] > max) return false; while (i <= nums.length - 1 && nums[j] > nums[i]) max = nums[i++]; nums[--i] = nums[j]; } return true; } - LeetCode 341 - Flatten Nested List Iterator
public class NestedIterator implements Iterator<Integer> { Stack<Iterator<NestedInteger>> stack; Integer nextInteger; public NestedIterator(List<NestedInteger> nestedList) { stack = new Stack<Iterator<NestedInteger>>(); stack.push(nestedList.iterator()); nextInteger = null; } public Integer next() { Integer next = null; if(hasNext()) { next = nextInteger; nextInteger=null; } return next; } public boolean hasNext() { if(nextInteger==null) { while(!stack.isEmpty()) { Iterator<NestedInteger> cIterator = stack.peek(); if(cIterator.hasNext()) { NestedInteger c = cIterator.next(); if(c.isInteger()) { nextInteger = c.getInteger(); return true; } else { stack.push(c.getList().iterator()); } } else stack.pop(); } return false; } else return true; } } - HARD LeetCode 394 - Decode String
public String decodeString(String s) { String res = ""; Stack<Integer> countStack = new Stack<>(); Stack<String> resStack = new Stack<>(); int idx = 0; while (idx < s.length()) { if (Character.isDigit(s.charAt(idx))) { int count = 0; while (Character.isDigit(s.charAt(idx))) { count = 10 * count + (s.charAt(idx) - '0'); idx++; } countStack.push(count); } else if (s.charAt(idx) == '[') { resStack.push(res); res = ""; idx++; } else if (s.charAt(idx) == ']') { StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder (resStack.pop()); int repeatTimes = countStack.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < repeatTimes; i++) { temp.append(res); } res = temp.toString(); idx++; } else { res += s.charAt(idx++); } } return res; } - LeetCode 653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST
- two stacks, two pointers + iterators
public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) { Stack<TreeNode> stackL = new Stack<TreeNode>(); // iterator 1 that gets next smallest value Stack<TreeNode> stackR = new Stack<TreeNode>(); // iterator 2 that gets next largest value for(TreeNode cur = root; cur != null; cur = cur.left) stackL.push(cur); for(TreeNode cur = root; cur != null; cur = cur.right) stackR.push(cur); while(stackL.size() != 0 && stackR.size() != 0 && stackL.peek() != stackR.peek()){ int tmpSum = stackL.peek().val + stackR.peek().val; if(tmpSum == k) return true; else if(tmpSum < k) for(TreeNode cur = stackL.pop().right; cur != null; cur = cur.left) stackL.push(cur); else for(TreeNode cur = stackR.pop().left; cur != null; cur = cur.right) stackR.push(cur); } return false; } - LeetCode 103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
- Queue + Dequeue
- dfs for fun: travel(TreeNode curr, List<List
> sol, int level)
- print directly: using 2 stacks
- or use 2 Dequeue
void printSpiral(Node node) { if (node == null) return; // NULL check // Create two stacks to store alternate levels // For levels to be printed from right to left Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>(); // For levels to be printed from left to right Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>(); // Push first level to first stack 's1' s1.push(node); // Keep printing while any of the stacks has some nodes while (!s1.empty() || !s2.empty()) { // Print nodes of current level from s1 and push nodes of // next level to s2 while (!s1.empty()) { Node temp = s1.peek(); s1.pop(); System.out.print(temp.data + " "); // Note that is right is pushed before left if (temp.right != null) s2.push(temp.right); if (temp.left != null) s2.push(temp.left); } // Print nodes of current level from s2 and push nodes of // next level to s1 while (!s2.empty()) { Node temp = s2.peek(); s2.pop(); System.out.print(temp.data + " "); // Note that is left is pushed before right if (temp.left != null) s1.push(temp.left); if (temp.right != null) s1.push(temp.right); } } }
- Queue + Dequeue
- LeetCode 430 - Flatten a multilevel linked list
public Node flatten(Node h) { if (h == null) return h; Stack<Node> st = new Stack<>(); Node prev = null; st.push(h); while (!st.isEmpty()){ Node cur = st.pop(); if (prev != null) { prev.next = cur; cur.prev = prev; prev.child = null; } if (cur.next != null) st.push(cur.next); if (cur.child != null) st.push(cur.child); prev = cur; } return h; }