How to Succeed in Algorithms Interview Series
Application of Interval
- sort by start time or finish time
- sort then choose greedily
- sort then dynamic programming
- track last max_end (or max_start)
- Two pointers for input data: int[] start, end
- TreeMap:
- start -> end, start/end -> index
- boundary count: point -> count
- TreeSet: intervals, sort by start or end time
- PriorityQueue
- merge k sorted list: [outerIndex, innerIndex]
- [point, isStart] or interval
- Greedy
- Boundary count: start +1, end -1;
- with TreeMap
Implementation
- List
merged, - save prevInterval, lastEnd
Basic
- LeetCode 57 - Insert Interval
- 3 steps: add intervals before the inserted, merge, add intervals after the inserted
public List<Interval> insert(List<Interval> intervals, Interval newInterval) { List<Interval> result = new LinkedList<>(); int i = 0; // add all the intervals ending before newInterval starts while (i < intervals.size() && intervals.get(i).end < newInterval.start) result.add(intervals.get(i++)); // merge all overlapping intervals to one considering newInterval while (i < intervals.size() && intervals.get(i).start <= newInterval.end) { newInterval = new Interval( // we could mutate newInterval here also Math.min(newInterval.start, intervals.get(i).start), Math.max(newInterval.end, intervals.get(i).end)); i++; } result.add(newInterval); // add the union of intervals we got // add all the rest while (i < intervals.size()) result.add(intervals.get(i++)); return result; } - LeetCode 56 - Merge Intervals
private class IntervalComparator implements Comparator<Interval> {
@Override
public int compare(Interval a, Interval b) {
return a.start < b.start ? -1 : a.start == b.start ? 0 : 1;
}
}
public List<Interval> merge(List<Interval> intervals) {
Collections.sort(intervals, new IntervalComparator());
LinkedList<Interval> merged = new LinkedList<Interval>();
for (Interval interval : intervals) {
if (merged.isEmpty() || merged.getLast().end < interval.start) {
merged.add(interval);
}
else {
merged.getLast().end = Math.max(merged.getLast().end, interval.end);
}
}
return merged;
}- LeetCode 436 - Find Right Interval
- TreeMap can simplify code related with binary search
public int[] findRightInterval(Interval[] intervals) { int[] result = new int[intervals.length]; java.util.NavigableMap<Integer, Integer> intervalMap = new TreeMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < intervals.length; ++i) { intervalMap.put(intervals[i].start, i); } for (int i = 0; i < intervals.length; ++i) { Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry = intervalMap.ceilingEntry(intervals[i].end); result[i] = (entry != null) ? entry.getValue() : -1; } return result; } - LeetCode 253 - Meeting Rooms II
public int minMeetingRooms(Interval[] intervals) { if (intervals == null || intervals.length == 0) { return 0; } TreeMap<Integer, Integer> times = new TreeMap<>(); for (Interval i : intervals) { times.put(i.start, times.getOrDefault(i.start, 0) + 1); times.put(i.end, times.getOrDefault(i.end, 0) - 1); } int count = 0, res = 0; for (int c : times.values()) { count += c; res = Math.max(res, count); } return res; }
Convert events into start, end array
- Put them into different arrays then two pointers
- PriorityQueue or sort all
- [LintCode] Number of Airplanes in the Sky
Sort
- Weighted Job Scheduling(Activity Selection Problem): Find the maximum profit subset of jobs such that no two jobs in the subset overlap
- LeetCode 218 - The Skyline Problem
- sweep line: Entering event h from large to small, Leaving event h from small to large
- TreeMap<Integer, Integer> heightMap: reverseOrder, height -> count
public List<int[]> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) { List<int[]> heights = new ArrayList<>(); for (int[] b: buildings) { heights.add(new int[]{b[0], - b[2]}); heights.add(new int[]{b[1], b[2]}); } Collections.sort(heights, (a, b) -> (a[0] == b[0]) ? a[1] - b[1] : a[0] - b[0]); TreeMap<Integer, Integer> heightMap = new TreeMap<>(Collections.reverseOrder()); heightMap.put(0,1);//detail int prevHeight = 0; List<int[]> skyLine = new LinkedList<>(); for (int[] h: heights) { if (h[1] < 0) { Integer cnt = heightMap.get(-h[1]); cnt = ( cnt == null ) ? 1 : cnt + 1; heightMap.put(-h[1], cnt); } else { Integer cnt = heightMap.get(h[1]); if (cnt == 1) { heightMap.remove(h[1]); } else { heightMap.put(h[1], cnt - 1); } } int currHeight = heightMap.firstKey(); if (prevHeight != currHeight) { skyLine.add(new int[]{h[0], currHeight}); prevHeight = currHeight; } } return skyLine; } - USACO 1.2 - Milking Cows: the longest continuous time of milking and the longest idle time
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {
Interval a = intervals[i];
if (a.getLow() <= high) {
high = Math.max(a.getHigh(), high);
} else {
maxInterval = Math.max(maxInterval, high - low);
maxGap = Math.max(maxGap, a.getLow() - high);
low = a.getLow();
high = a.getHigh();
}
}TreeMap
- start -> end
- boundary count, position -> count+1 for start, count-1 for end
Methods of TreeMap
- floorKey, ceilingKey, lowerEntry,
LeetCode 729 - My Calendar I
- TreeMap: start -> end (interval tree) ##### LeetCode 731 - My Calendar II: not cause a triple booking
- List<int[]> booked, dbooked;
List<int[]> calendar;
List<int[]> overlaps;
MyCalendarTwo() {
calendar = new ArrayList();
}
public boolean book(int start, int end) {
for (int[] iv: overlaps) {
if (iv[0] < end && start < iv[1]) return false;
}
for (int[] iv: calendar) {
if (iv[0] < end && start < iv[1])
overlaps.add(new int[]{Math.max(start, iv[0]), Math.min(end, iv[1])});
}
calendar.add(new int[]{start, end});
return true;
}
// -------
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> delta;
public MyCalendarTwo() {
delta = new TreeMap();
}
public boolean book(int start, int end) {
delta.put(start, delta.getOrDefault(start, 0) + 1);
delta.put(end, delta.getOrDefault(end, 0) - 1);
int active = 0;
for (int d: delta.values()) {
active += d;
if (active >= 3) {
delta.put(start, delta.get(start) - 1);
delta.put(end, delta.get(end) + 1);
if (delta.get(start) == 0)
delta.remove(start);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}LeetCode 732 - My Calendar III
- boundary count
LeetCode 352. Data Stream as Disjoint Intervals
- TreeMap: start -> Interval
LeetCode 715 - Range Module
Boundary count
- boundary count, position -> count+1 for start, count-1 for end
- critical point: cnt=0 or cnt itself
- sort, TreeMap or PriorityQueue
PriorityQueue
- multiple already sorted list: merge k sorted list
- LeetCode 759 - Employee Free Time
public List<Interval> employeeFreeTime(List<List<Interval>> schedule) {
List<Interval> res = new ArrayList<Interval>();
PriorityQueue<Node> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Node>(
(a, b) -> schedule.get(a.employee).get(a.index).start - schedule.get(b.employee).get(b.index).start);
int start = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < schedule.size(); i++) {
minHeap.add(new Node(i, 0));
start = Math.min(start, schedule.get(i).get(0).start);
}
while (!minHeap.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = minHeap.poll();
if (start < schedule.get(cur.employee).get(cur.index).start) {
res.add(new Interval(start, schedule.get(cur.employee).get(cur.index).start));
}
start = Math.max(start, schedule.get(cur.employee).get(cur.index).end);
cur.index++;
if (cur.index < schedule.get(cur.employee).size()) {
minHeap.add(cur);
}
}
return res;
}
class Node {
int employee;
int index;
public Node(int employee, int index) {
this.employee = employee;
this.index = index;
}
}Greedy
- LeetCode 435 - Non-overlapping Intervals
- find the minimum number of intervals you need to remove to make the rest of the intervals non-overlapping
- same as find the maximum number of intervals that are non-overlapping
- https://zhuhan0.blogspot.com/2017/03/leetcode-non-overlapping-intervals.html
- LeetCode 452 - Minimum Number of Arrows to Burst Balloons
- We have to shoot down every balloon, so for each ballon there must be an arrow whose position is between balloon[0] and balloon[1] inclusively
- LeetCode 646 - Maximum Length of Pair Chain
- sort then greedy: O(nlogn)
- sort + stack
- sort then dp: O(n^2) dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i][k]+1 when pairs[k][1] < pairs[j][0])
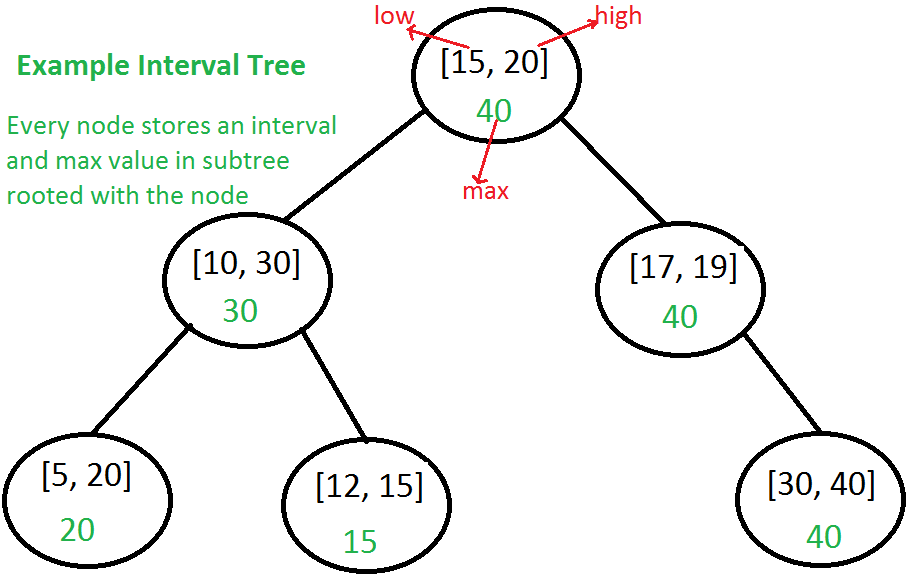
Interval Tree
- Augmented BST: [start, end, max_end], sorted by start and with max: Maximum high value in subtree rooted with this node
- Use TreeMap in simple case
- Interval trees are mainly optimized for overlapping queries for a given interval
- Segment tree is mainly optimized for queries for a given point
- Given n appointments, find all conflicting appointments
- Google – Toggle Bubbles Problem