Monotone Queue + Stack - How to Succeed in Algorithms Interview
States
- what to store
- element, index
- candidates of starting index/element
- prefix sum: not necessarily use the input data
- running length: element(or index), count of same values
Partial Monotonic stack/queue
When to use
- expect time complexity O(N)
- find one range with xxx
Monotonic Queue Examples
DP - Monotone Queue
- F[i]=min(F[j]+a[i]:j<i) a[i]是与j无关的数
- moving interval
- NOIP - 烽火传递
- JZOJ 1772 - Holiday
- bzoj 3831 - Little Bird
Examples
- LeetCode 239 - Sliding Window Maximum
- HARD LeetCode 862 - Shortest Subarray with Sum at Least K
public int shortestSubarray(int[] A, int K) {
int N = A.length;
long[] P = new long[N+1];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
P[i+1] = P[i] + (long) A[i];
// Want smallest y-x with P[y] - P[x] >= K
int ans = N+1; // N+1 is impossible
Deque<Integer> monoq = new LinkedList(); //opt(y) candidates, as indices of P
for (int y = 0; y < P.length; ++y) {
// Want opt(y) = largest x with P[x] <= P[y] - K;
while (!monoq.isEmpty() && P[y] <= P[monoq.getLast()])
monoq.removeLast();
while (!monoq.isEmpty() && P[y] >= P[monoq.getFirst()] + K)
ans = Math.min(ans, y - monoq.removeFirst());
monoq.addLast(y);
}
return ans < N+1 ? ans : -1;
}
Monotonic Stack
- stack + greedy
- the answer is known when the element is popped out
- Focus on the element pushed in or popped out ##### When to use
- 单调栈这种数据结构,通常应用在一维数组上, 通常当前元素和前后元素之间的大小关系有关系的话
- 每个元素出栈时候的意义
- 对每一个节点进行扩展的问题
- look for range with smallest/largest and xxx
Implementation
- calculate results when pop the element from the stack
- < or <=; > or >=
Examples
public int sumSubarrayMins(int[] A) {
int res = 0, n = A.length, mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
int[] left = new int[n], right = new int[n];
Stack<int[]> s1 = new Stack<>(), s2 = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int count = 1;
while (!s1.isEmpty() && s1.peek()[0] > A[i])
count += s1.pop()[1];
s1.push(new int[] {A[i], count});
left[i] = count;
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
int count = 1;
while (!s2.isEmpty() && s2.peek()[0] >= A[i])
count += s2.pop()[1];
s2.push(new int[] {A[i], count});
right[i] = count;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
res = (res + A[i] * left[i] * right[i]) % mod;
return res;
}
public int sumSubarrayMins(int[] A) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int[] dp = new int[A.length + 1];
stack.push(-1); // case when stack is empty, not really needed
int result = 0, M = (int)1e9 + 7;
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
while (stack.peek() != -1 && A[i] <= A[stack.peek()]) {
stack.pop();
}
dp[i + 1] = (dp[stack.peek() + 1] + (i - stack.peek()) * A[i]) % M;
stack.push(i);
result += dp[i + 1];
result %= M;
}
return result;
}
public int sumSubarrayMins(int[] A) {
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<>();
int n = A.length, res = 0, mod = (int)1e9 + 7, j,k;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
while (!s.isEmpty() && A[stack.peek()] > (i == n ? 0 : A[i])) {
j = stack.pop();
k = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
res = (res + A[j] * (i - j) * (j - k)) % mod;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return res;
}
public int trap(int[] A) {
if (A==null) return 0;
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
int i = 0, maxWater = 0, maxBotWater = 0;
while (i < A.length){
if (s.isEmpty() || A[i]<=A[s.peek()]){
s.push(i++);
}
else {
int bot = s.pop();
maxBotWater = s.isEmpty()? // empty means no il
0:(Math.min(A[s.peek()],A[i])-A[bot])*(i-s.peek()-1);
maxWater += maxBotWater;
}
}
return maxWater;
}
- LeetCode 85 - Maximal Rectangle
- calculate maxArea for each row
- Separate DP functions/states
- left(i,j) = max(left(i-1,j), cur_left), cur_left can be determined from the current row
- right(i,j) = min(right(i-1,j), cur_right), cur_right can be determined from the current row
- height(i,j) = height(i-1,j) + 1, if matrix[i][j]==‘1’;
- LeetCode 402 - Remove K Digits
public String removeKdigits(String num, int k) {
int len = num.length();
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
int i =0;
while(i<num.length()){
//whenever meet a digit which is less than the previous digit, discard the previous one
while(k>0 && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()>num.charAt(i)){
stack.pop();
k--;
}
stack.push(num.charAt(i));
i++;
}
// corner case like "1111"
while(k>0){
stack.pop();
k--;
}
//construct the number from the stack
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while(!stack.isEmpty())
sb.append(stack.pop());
sb.reverse();
//remove all the 0 at the head
while(sb.length()>1 && sb.charAt(0)=='0')
sb.deleteCharAt(0);
return sb.toString();
}
- LintCode 126 - Max Tree
public TreeNode maxTree(int[] A) {
if (A == null || A.length == 0) return null;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
//遍历A的每个元素,创造结点node
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(A[i]);
//将stack中小于当前结点的结点都pop出来,存为当前结点的左子树
while (!stack.isEmpty() && node.val >= stack.peek().val) node.left = stack.pop();
//如果stack仍非空,剩下的结点一定大于当前结点,所以将当前结点存为stack中结点的右子树;而stack中结点本来的右子树之前已经存为当前结点的左子树了
if (!stack.isEmpty()) stack.peek().right = node;
//stack中存放结点的顺序为:底部为完整的max tree,从下向上是下一层孩子结点的备份,顶部是当前结点的备份
stack.push(node);
}
TreeNode root = stack.pop();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) root = stack.pop();
return root;
}
- LeetCode 316 - Remove Duplicate Letters
- remove duplicate letters so that every letter appear once and only once. You must make sure your result is the smallest in lexicographical order among all possible results
- LeetCode 321 - Create Maximum Number
- Given two arrays of length m and n with digits 0-9 representing two numbers. Create the maximum number of length k <= m + n from digits of the two. The relative order of the digits from the same array must be preserved. Return an array of the k digits. You should try to optimize your time and space complexity.
- HARD LeetCode 654 - Maximum Binary Tree
- decreasing stack
- create the TreeNode while access the data, push them into monotone stack, connect TreeNodes when push or pop
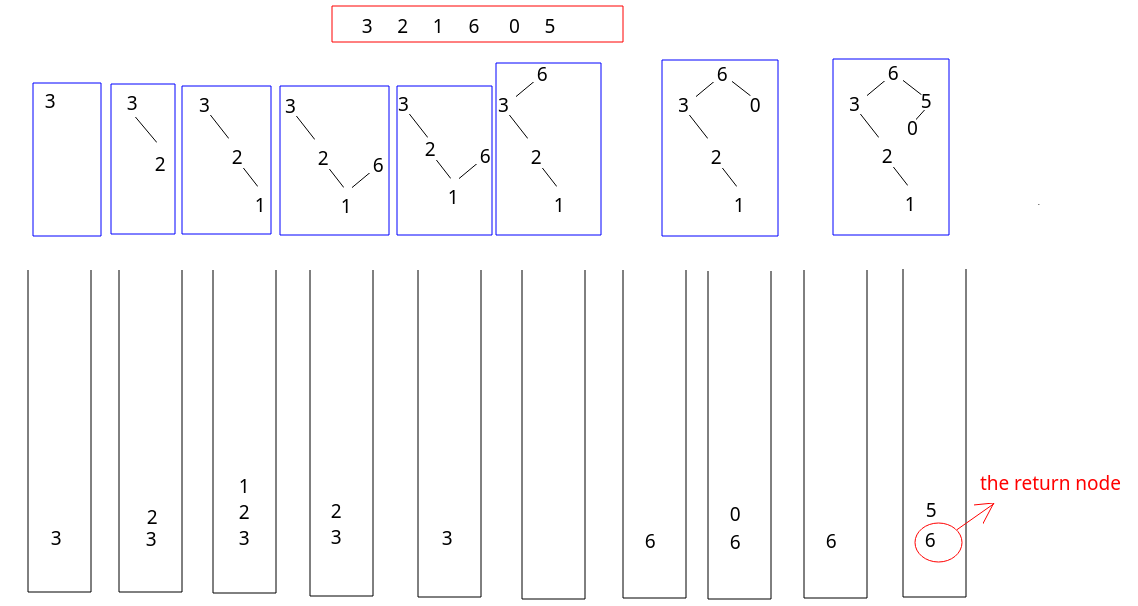
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
TreeNode curr = new TreeNode(nums[i]);
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().val < nums[i]) {
curr.left = stack.pop();
}
if(!stack.isEmpty()) {
stack.peek().right = curr;
}
stack.push(curr);
}
return stack.isEmpty() ? null : stack.removeLast();
}
- HARD LeetCode 456 - 132 Pattern - hard
public boolean find132pattern(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length < 3)
return false;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int[] min = new int[nums.length];
min[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++)
min[i] = Math.min(min[i - 1], nums[i]);
for (int j = nums.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (nums[j] > min[j]) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() <= min[j])
stack.pop();
if (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() < nums[j])
return true;
stack.push(nums[j]);
}
}
return false;
}
// https://www.jianshu.com/p/910fe372d9a0
public boolean find132pattern(int[] nums) {
boolean result = false;
int third = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // the third number, 13(2)
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); // decreasing stack
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (nums[i] < third)
return true;
while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i] > stack.peek()) {
third = Math.max(third, stack.pop());
}
stack.push(nums[i]);
}
return result;
}
Monotonic stack stores candidates then scan original data from end
int[] res, count; ArrayList<HashSet<Integer>> tree; int n;
public int[] sumOfDistancesInTree(int N, int[][] edges) {
tree = new ArrayList<HashSet<Integer>>();
res = new int[N];
count = new int[N];
n = N;
for (int i = 0; i < N ; ++i ) tree.add(new HashSet<Integer>());
for (int[] e : edges) {tree.get(e[0]).add(e[1]); tree.get(e[1]).add(e[0]);}
dfs(0, new HashSet<Integer>());
dfs2(0, new HashSet<Integer>());
return res;
}
public void dfs(int root, HashSet<Integer> seen) {
seen.add(root);
for (int i : tree.get(root))
if (!seen.contains(i)) {
dfs(i, seen);
count[root] += count[i];
res[root] += res[i] + count[i];
}
count[root]++;
}
public void dfs2(int root, HashSet<Integer> seen) {
seen.add(root);
for (int i : tree.get(root))
if (!seen.contains(i)) {
res[i] = res[root] - count[i] + n - count[i];
dfs2(i, seen);
};
}
